 |
Plant Physiology (Biology 327)
- Dr. Stephen G. Saupe; College of St. Benedict/ St.
John's
University; Biology Department; Collegeville, MN 56321; (320) 363 - 2782;
(320) 363 - 3202, fax;
ssaupe@csbsju.edu |
Protoplasts: Pre-Lab Preparation
I. Readings. To prepare for this lab you should read:
- Print copies of all materials for Lab 3.
Read these materials and bring copies to lab.
- Read any appropriate background information (text,
articles) as necessary
- You may want to print copies of
equations and
conversions and exponential numbers
II. Additional Preparation. It would be helpful to review:
- the operation of a compound light microscope
- carbohydrate structure and chemistry
- the use of the spectrophotometer
- simple statistical procedures (i.e., mean, standard deviation). Visit the
statistics web site for the Biology
department, and/or check the articles in the filing cabinet.
III. Questions: (Answer on a separate sheet; show your work)
- List the organelles you expect to see in a plant cell or protoplast with a light
microscope.
- What determines plant cell shape?
- What shape do you predict for the protoplasts? Why?
- How many grams of sucrose (MW = 342) is required to make 1.0 liter of a 0.5 M sucrose
solution?
- How many grams of sucrose is required to make 1 liter of a 25% sucrose solution? What is
the molarity of this solution?
- What is cyclosis and do you expect to observe it in the protoplasts?
- What types of contaminants do you expect to find in the initial protoplast suspension?
- Draw the chemical structures of sucrose, mannitol and glucose.
- Make a flow chart depicting, in general terms, a protocol that could be used to
determine the concentration of nitrate in a leaf vacuole.
- The protoplast membrane is permeable to neutral red (True/False)
- The protoplast membrane is permeable to Evan's blue (True/False)
- The tonoplast is permeable to neutral red (True/False)
- Define: transvacuolar strand, cellulase, pectinase, hemicellulase.
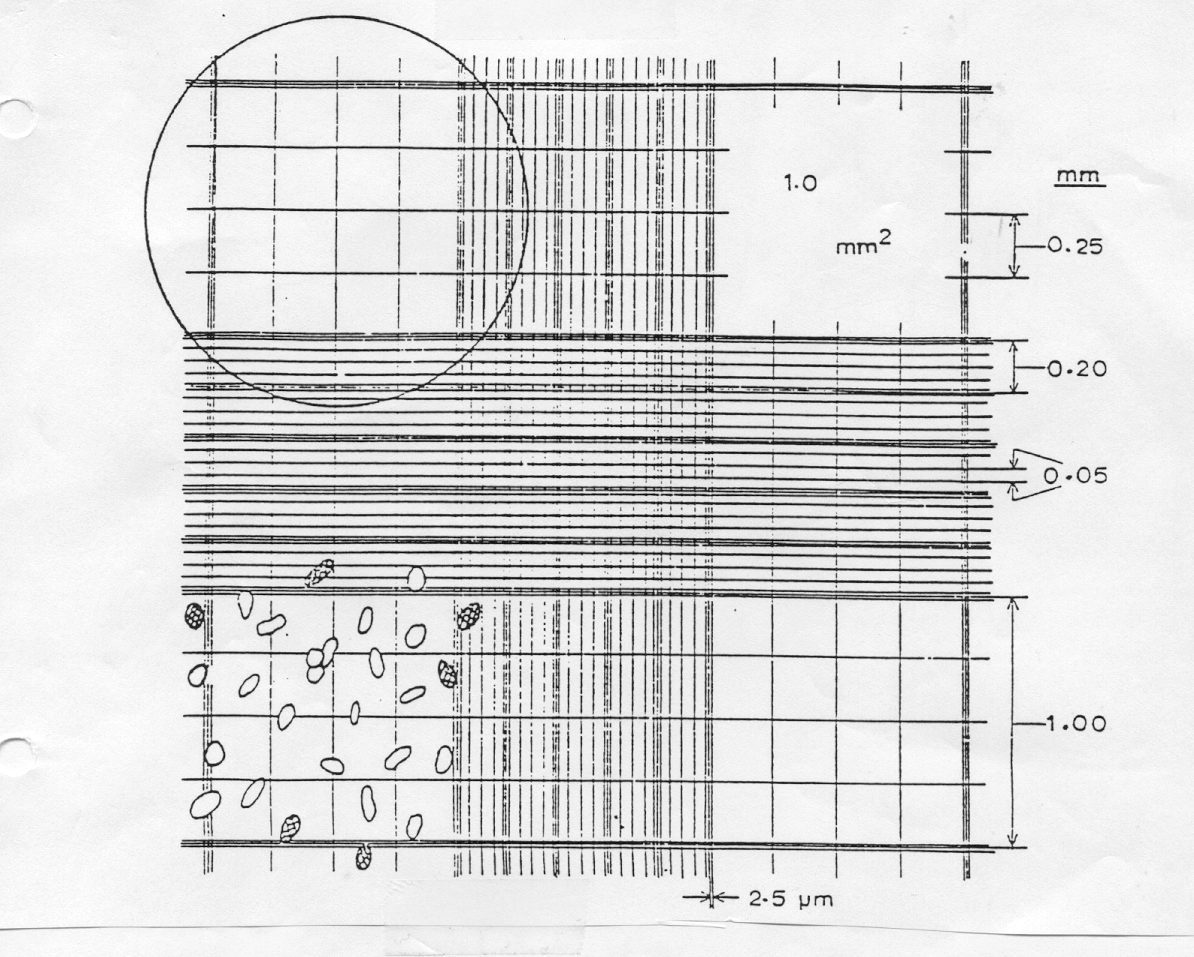
- If the objects in Figure 1 in the hemocytometer write-up are chloroplasts, what is their
concentration (chloroplasts � mL-1 )? Assume no dilution. SHOW
YOUR WORK.
- Wagner (Plant Physiol. 64:88; 1979) reports that the average diameters of tulip leaf
protoplasts and vacuoles are 80 �m and 75 �m, respectively. (SHOW
YOUR WORK)
- Calculate the volume (�m3) of a
protoplast ______________
- Calculate the surface area (�m2) of a protoplast _________
- Calculate the volume (�m3) of a vacuole ________________
- What percent of the protoplast volume does the vacuole occupy in tulip leaf cells?
____________
- Imagine that the vacuoles are placed in a hypotonic medium
and swell to a diameter of 90 �m. How much water (expressed in units of
�m3 or nL) diffused
into the vacuole? _______________
- The average concentration of glucose in a vacuole is 150 mM. What will be the new
concentration of glucose (mM) in the vacuole after they absorb water (see E above) ?
______________
16. Moskowitz and Hrazdina (Plant Physiol. 68:686; 1981) studied the vacuolar contents
of cells from the skins of DeChaunac grapes. In their protocol, from 200 mature grape
skins they obtained 1.5 X 107 vacuoles which was a yield of approximately 5%.
SHOW YOUR WORK.
- Calculate the number of cells per grape skin ___________
- The average diameter of a vacuole was 32 �m. What is its volume? __________ (�m3) = ___________ (pL)
- They homogenized a sample of containing 15.7 X 106 vacuoles and found that it
had an anthocyanin content of 2.62 x 10-5 mol. What is the anthocyanin content
(pmol) in each vacuole?____________
- What is the vacuolar concentration (Molarity) of anthocyanin? __________ M or __________
mM
- Of the eight cations studied, Moskowitz and Hrazdina observed low concentrations except
for potassium which they determined to be 46.3 pmol/vacuole. What is the molar
concentration (M) of potassium in the vacuole? ____________
- Magnesium had the next highest concentration in the vacuole, but it was only 2% of the
potassium concentration. What was its molar concentration (M) in the vacuole? _________
Last updated:
01/07/2009 � Copyright by SG
Saupe


